R2 2013 høst LØSNING: Forskjell mellom sideversjoner
| Linje 132: | Linje 132: | ||
\displaystyle \Rightarrow Vt_2 + 3 = -\frac{11}{2}x + 11 \\ | \displaystyle \Rightarrow Vt_2 + 3 = -\frac{11}{2}x + 11 \\ | ||
\displaystyle \Rightarrow Vt_2 = -\frac{11}{2}x + 8$ | \displaystyle \Rightarrow Vt_2 = -\frac{11}{2}x + 8$ | ||
===Oppgave 7=== | |||
==DEL TO== | ==DEL TO== | ||
Sideversjonen fra 19. feb. 2014 kl. 00:15
Matteprat: Diskusjon omkring denne oppgaven
DEL EN
Oppgave 1
a) $ \displaystyle f(x) = 5x\cos x$
Produktregelen for derivasjon gir at
$ \displaystyle f'(x) = 5\cos x + 5x(- sin x) = 5\cos x - 5x\sin x = 5(cos x - x\sin x)$
b) $ \displaystyle g(x) = \frac{sin (2x)}{x}$
Brøkregelen for derivasjon gir at
$ \displaystyle g'(x) = \frac{2\cos (2x) \cdot x - sin (2x) \cdot 1}{x^2} = \frac{2x cos (2x) - sin (2x)}{x^2}$
Oppgave 2
a) $ \displaystyle \int_0^{1} 2e^{2x} \, \mathrm{d} = 2 \int_0^{1} e^{2x} \, \mathrm{d}x = 2 \left[ \frac{1}{2}e^{2x} \right]_0^{1} = \frac{2}{2} \left[e^{2x} \right]_0^{1} = e^{2 \cdot 1} - e^{2 \cdot 0} = e^2 - 1$
b) $ \displaystyle \int 2x \cdot e^x \, \mathrm{d}x$
$\displaystyle u = 2x$ og $\displaystyle v' = e^x$. Delvis integrasjon gir
$\displaystyle \int 2x \cdot e^x \, \mathrm{d}x = 2x \cdot e^x - \int 2e^x \, \mathrm{d}x + C = 2xe^x - 2\int e^x \, \mathrm{d}x + C = 2xe^x - 2e^x + C = 2e^x(x - 1) + C$
Oppgave 3
a) $\vec{AB} = \left[-2,3,0\right]$ og $\vec{AC} = \left[-2,0,4\right]$
Da blir $\vec{AB} \cdot \vec{AC} = (-2) \cdot (-2) + 3 \cdot 0 + 0 \cdot 4 = 4$
og $\vec{AB} \times \vec{AC} = \left[3\cdot4 - 0\cdot0,-\left((-2)\cdot4 - 0\cdot(-2)\right),(-2)\cdot0 - 3\cdot(-2)\right] = \left[12,8,6\right]$
b) $ \displaystyle V = |\frac{1}{6}(\vec{AB} \times {AC})\cdot\vec{AO}| \\ \displaystyle = |\frac{1}{6}\left[12,8,6\right]\cdot\left[-2,0,0\right]| \\ \displaystyle = |\frac{1}{6}\left(12(-2) + 8\cdot0 0+ 6\cdot0\right)| \\ \displaystyle = |\frac{1}{6}(-24) \\ \displaystyle = |- \frac{24}{6}| \\ \displaystyle = |-4| \\ \displaystyle = 4$
Eventuelt kan man regne ut volumet ved hjelp av formelen for volum av pyramide, $V = \frac{G\cdot h}{3}$,
hvor $ \displaystyle G = \frac{|\vec{OA}|\cdot|\vec{OB|}}{2} = \frac{2\cdot3}{2} = 3$ og $ \displaystyle h = |\vec{OC}| = 4$.
Da får man $ \displaystyle V = \frac{3\cdot4}{3} = 4$
c) Om man bruker punktet $A(2,0,0)$ og normalvektoren $\vec{AB} \times \vec{AC} = \left[12,8,6\right]$ blir likningen for planet $\alpha$:
$ \displaystyle 12(x - 2) + 8(y - 0) + 6(z - 0) = 0 \\ \displaystyle 12x - 24 + 8y + 6z = 0 \\ \displaystyle 12x + 8y + 6z = 24 \\ \displaystyle \frac{12x}{24} + \frac{8y}{24} + \frac{6z}{24} = \frac{24}{24} \\ \displaystyle \frac{x}{2} + \frac{y}{3} + \frac{z}{4} = 1$
Hvilket skulle vises.
Oppgave 4
a) Rekken er geometrisk fordi neste ledd i rekken genereres ved å multiplisere det forrige leddet med en fast kvotient $\displaystyle k = e^{-1} = \frac{1}{e}$. Ettersom $\displaystyle \frac{1}{e} < 1$, er altså $\displaystyle |k|<1$, hvilket gjør rekken konvergent.
$ \displaystyle S = \frac{a_1}{1-k} = \frac{1}{1-\frac{1}{e}} = \frac{1}{\frac{e}{e} - \frac{1}{e}} = \frac{1}{\frac{e-1}{e}} =\frac{e}{e-1}$
b) I dette tilfellet er $\displaystyle k = e^{-x}$, og rekken er konvergent dersom $\displaystyle |k|<1$.
$ \displaystyle |e^{-x}|<1$
Ettersom $\displaystyle e^{-x}$ alltid vil være positivt, kan man skrive om likningen til
$ \displaystyle e^{-x}<1 \\ \displaystyle \ln(e^{-x})<\ln1 \\ \displaystyle (-x)\cdot\ln(e)<0 \\ \displaystyle -x<0 \\ \displaystyle x>0$
$ \displaystyle S = \frac{a_0}{1-k} = \frac{1}{1-e^{-x}} =\frac{1}{1-\frac{1}{e^x}} = \frac{1}{\frac{e^x}{e^x} - \frac{1}{e^x}} = \frac{1}{\frac{e^{x}-1}{e^{x}}} = \frac{e^x}{e^x - 1}$
Oppgave 5
$\displaystyle N'(t) = 4t + 3$ og $\displaystyle N(0) = 800$
$\displaystyle N(t) = \int (4t + 3)dx \\ \displaystyle N(t) = 2t^2 + 3t + C \\$
$\displaystyle N(0) = 800 \\
\displaystyle 2\cdot0^2 + 3\cdot0 + C = 800 \\
\displaystyle 0 + 0 + C = 800 \\
\displaystyle C = 800 \Rightarrow N(t) = 2t^2+3t + 800\\$
$\displaystyle N(10) = 2\cdot10^2 + 3\cdot10 + 800 = 200 + 30 + 800 = 1030$
Det var altså 1030 individer i populasjonen etter 10 timer.
Oppgave 6
$ \displaystyle f(x) = \frac{1}{2}x^4 - 2x^3 + \frac{5}{2}x$
a) $\displaystyle f'(x) = 2x^3 - 6x^2 + \frac{5}{2}$
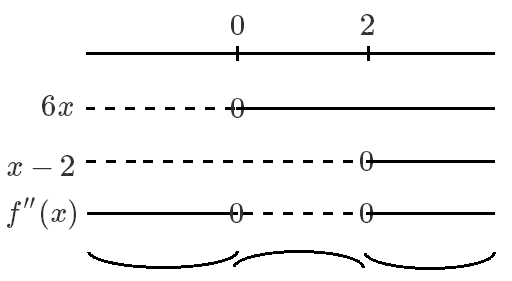
$\displaystyle f ' ' (x) = 6x^2 - 12x = 6x\left(x - 2\right)$
Vendepunkter:
$\displaystyle Vp_1: \left(0,f(0)\right) = \left(0,\frac{1}{2}\cdot0^4 - 2\cdot0^3 + \frac{5}{2}\cdot0\right) = \left(0,0\right)$
$\displaystyle Vp_2: \left(2,f(2)\right) = \left(2,\frac{1}{2}\cdot2^4 - 2\cdot2^3 + \frac{5}{2}\cdot2\right) = \left(2,-3\right)$
b) $\displaystyle Vt_1 - 0 = f ' (0)\cdot(x - 0) \Rightarrow Vt_1 = \left(2\cdot0^3 - 6\cdot0^2 + \frac{5}{2}\right)x \Rightarrow Vt_1 = \frac{5}{2}x$
$\displaystyle Vt_2 - \left(-3\right) = f ' (2)\cdot(x - 2) \\
\displaystyle \Rightarrow Vt_2 + 3 = \left(2\cdot2^3 - 6\cdot2^2 + \frac{5}{2}\right)\left(x - 2\right) \\
\displaystyle \Rightarrow Vt_2 + 3 = -\frac{11}{2}\left(x - 2\right) \\
\displaystyle \Rightarrow Vt_2 + 3 = -\frac{11}{2}x + 11 \\
\displaystyle \Rightarrow Vt_2 = -\frac{11}{2}x + 8$